Simulation test study on filling flow law of gangue slurry in goaf
Seepage process and characteristics of slurry
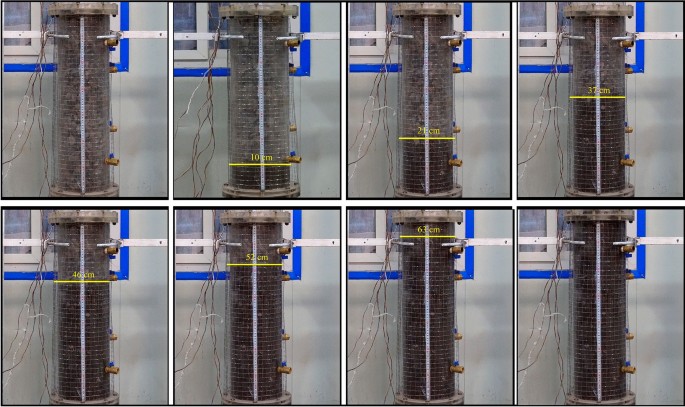
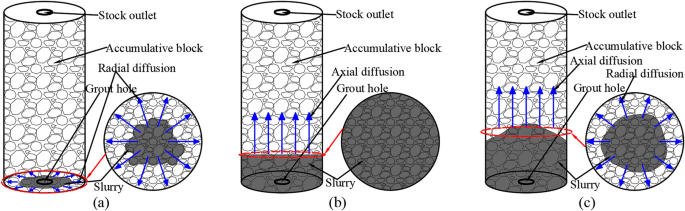
According to the flow law of gangue slurry in the visual grouting test column in the grouting test process (Fig. 8), it can be divided into three stages, which are interrelated and inseparable. When the gangue slurry is initially injected, the gangue slurry takes the grouting mouth as the circle center and diffuses around the void of the simulated rock block. This stage is called the radial diffusion stage43, as shown in Fig. 9a. When the gangue slurry reaches the boundary of the simulated rock void, the diffusion front of the slurry begins to find the dominant path, that is, it permeates and diffuses to the void channel with lower flow resistance, showing an uneven axial diffusion flow characteristic. This stage is called the axial diffusion stage, as shown in Fig. 9b. In the process of axial flow diffusion of gangue slurry, when the body weight of the slurry, the simulated self-gravity and void resistance of the upper part of the slurry are greater than the simulated lateral resistance of the void of the slurry in the process of radial diffusion of the slurry, the slurry will flow into the surrounding void and squeeze the rock block. There are both radial diffusion and axial diffusion flow characteristics, and this stage is called the bidirectional diffusion stage, as shown in Fig. 9c.
After the grouting test, the mixture of simulated accumulated rock and gangue slurry in the test column was taken out, and the slurry was evenly filled into the void of simulated accumulated rock mass to form uniform grouting plus solid, and the grouting and filling effect was good, as shown in Figure 10.
Variation of slurry flow diffusion velocity
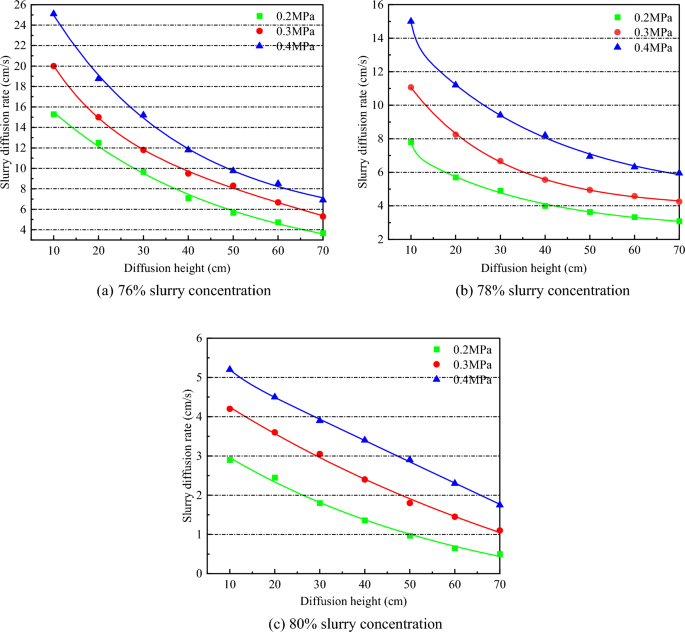
Under the same grouting pressure condition, the flow velocity changes of 76%, 78%, and 80% slurry with different concentrations are compared. The test results are shown in Table 5.
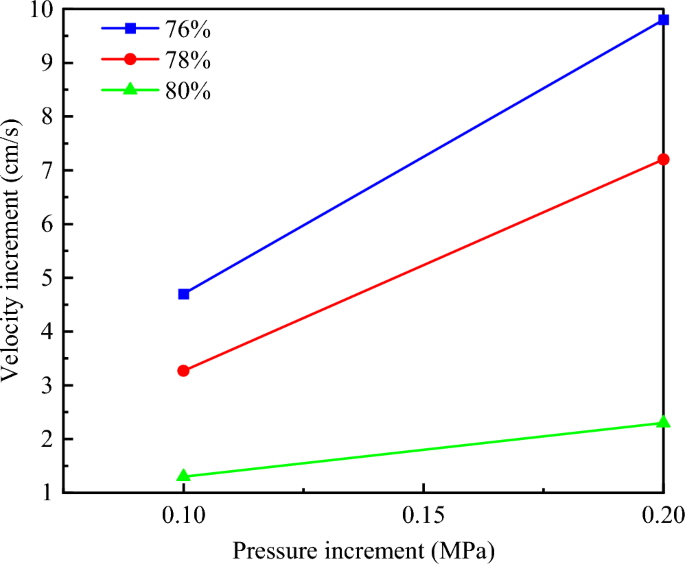
It can be seen from the analysis of Fig. 11 that the flow velocity of slurry with different concentrations is different under the same grouting pressure, and the larger the slurry concentration, the smaller the slurry flow velocity. With the increase of grouting pressure, the flow rate of slurry with different concentrations increases. Taking the slurry flow velocity at the diffusion height of 10 cm as an example, the slurry flow velocity of 76% slurry at 0.2 MPa grouting pressure was 15.3 cm/s, and that at 0.3 MPa and 0.4 MPa grouting pressure was 20 cm/s and 25.1 cm/s, respectively, increasing by 30.72% and 64.05%. The slurry flow velocity of 78% slurry was 7.8 cm/s under 0.2 MPa grouting pressure, and 11.07 cm/s and 15 cm/s under 0.3 MPa and 0.4 MPa grouting pressure, increasing by 41.92% and 92.31%, respectively. The slurry flow velocity of 80% concentration slurry was 2.9 cm/s under 0.2 MPa grouting pressure, and 4.2 cm/s and 5.2 cm/s under 0.3 MPa and 0.4 MPa grouting pressure, which increased by 44.83% and 79.31%, respectively. There is a linear relationship between the growth rate of slurry flow velocity of the three concentrations and the growth rate of grouting pressure, as shown in Fig. 12. Moreover, under the condition of the same pressure increase, the larger the slurry concentration, the lower the growth rate of flow velocity.
There is a nonlinear relationship between slurry velocity and slurry diffusion distance, which indicates that the flow of gangue slurry in the accumulated rock mass is nonlinear, and slurry velocity decreases gradually with the increase of diffusion distance. This is because the voidage of the accumulated rock mass is a constant value. As the slurry permeates into the voidage of the accumulated rock mass, the voidage gradually decreases and the flow resistance gradually increases, resulting in the gradual attenuation of the slurry velocity, and the attenuation rate decreases with the increase of the diffusion distance. Under the condition of the same slurry concentration, the greater the grouting pressure, the faster the slurry velocity decay rate. Therefore, in the actual engineering grouting, it is necessary to design the viscosity parameters of the slurry to control the grouting efficiency and implementability.
Change law of void pressure
The 78% concentration gangue slurry was selected to compare the change rule of void pressure between the stacked rock blocks with the grouting time during the grouting process under the three grouting pressures of 0.2 MPa, 0.3 MPa, and 0.4 MPa. The dynamic change curve of its internal pressure…
Read More: Simulation test study on filling flow law of gangue slurry in goaf