Physical properties, engine performance, and exhaust emissions of waste fish oil
Fuels properties
According to the GC analysis, the main fatty acid esters of WFO biodiesel are palmitic acid, and trans-9-Elaidic acid methyl ester. The presence of Myristic acid methyl ester in the WFO biodiesel is also confirmed. More details regarding the fatty acid profiles and the compositional analysis of the WFO biodiesel can be found in the supporting information file.
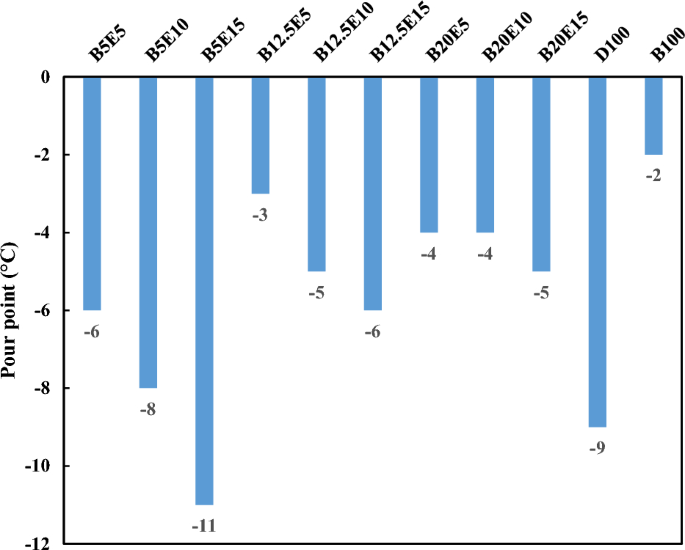
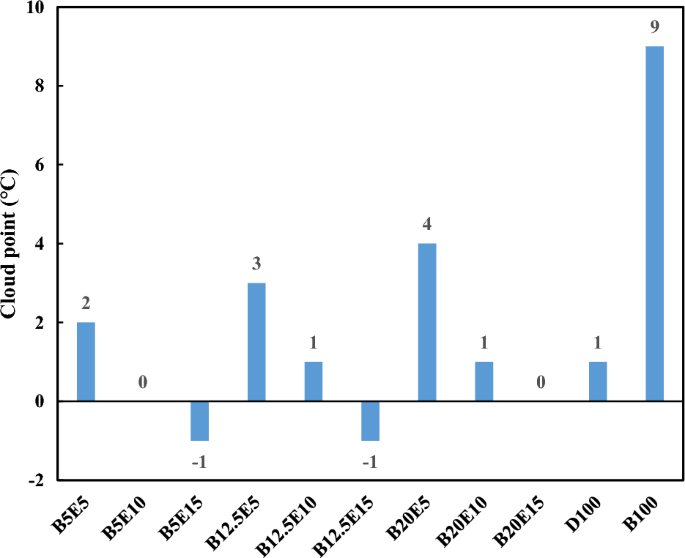
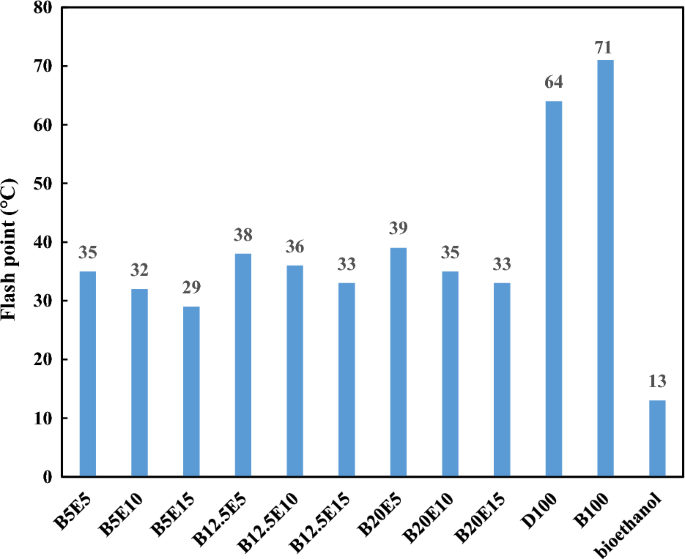
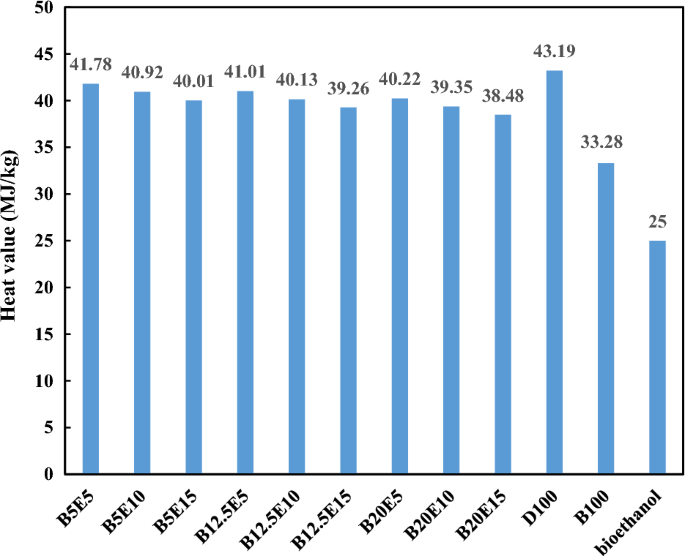
In the present study, different fuel blends were prepared by mixing different concentration of WFO biodiesel, bioethanol, and petro-diesel. Table 2 shows the detailed composition of different WFO biodiesel/bioethanol/diesel fuel samples. Afterwards, different specifications such as density, kinematic viscosity, pour point, cloud point, and flash point were measured for different fuel blends according to ASTM D 4052, ASTM D 445-06, ASTM D 97, ASTM D 2500, and ASTM D93 standards, respectively. The results of these measurements are presented in Figs. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 for different examined fuel samples. The range of WFO biodiesel in the ternary fuel blends is 5–20%. The range of bioethanol in the ternary fuel samples is 5–15%. These selected concentration ranges are considerably wider compared to Sathiyaseelan et al.20 study.
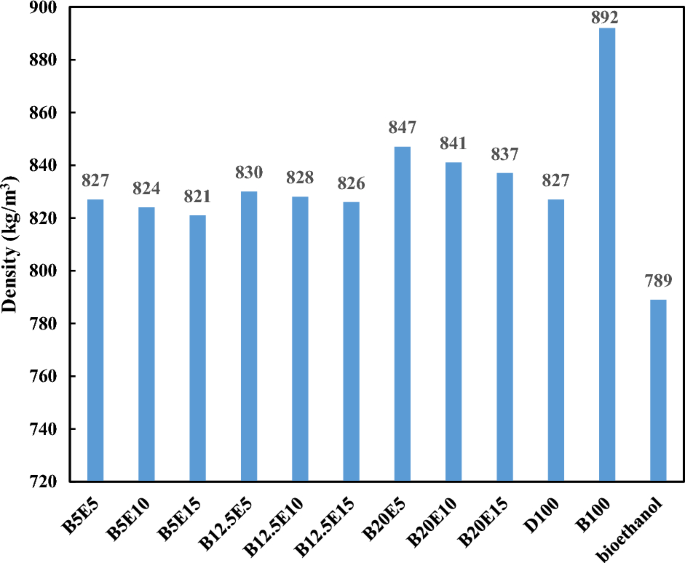
Figure 2 shows the density of different examined fuel samples. It should be noted that the fuel density directly affect the injection timing, and spray quality of fuels in the combustion chamber28,29. Fuel density also affect the exhaust emissions. Using high density fuel results in increasing the amount of fuel entering the combustion chamber and it gets the oxygen to fuel ratio out of balance, which leads to incomplete combustion and subsequent increment in the emission of unburned hydrocarbons28. According to Fig. 2, the density of fuel blends increases by an increment in the WFO biodiesel content of blends because the density of WFO biodiesel is higher than the neat diesel due to higher molecular weight of WFO biodiesel compared to neat diesel30. The density of biodiesel produced from different sources are in the same range but the WFO biodiesel (density = 892 kg/m3) is more suitable for the fuel blends preparation compared to the soybean biodiesel (density = 913 kg/m3) and the pongamia biodiesel (density = 931 kg/m3)8. On the other hand, the density of ternary fuel blends decreases by an increment in the bioethanol content of blend due to lower density of bioethanol compared to diesel and WFO biodiesel. The addition of bioethanol leads to an improvement in the fuel blend/air mixing due to its low density which results in more complete combustion close to the stoichiometric ratio and subsequent decrease in the exhaust smoke31. According to Fig. 2, it was also found that the bioethanol addition to the ternary fuel blends neutralizes the density increment of WFO biodiesel addition. In this regard, the lowest value of density is observed for B5E15 fuel blends.
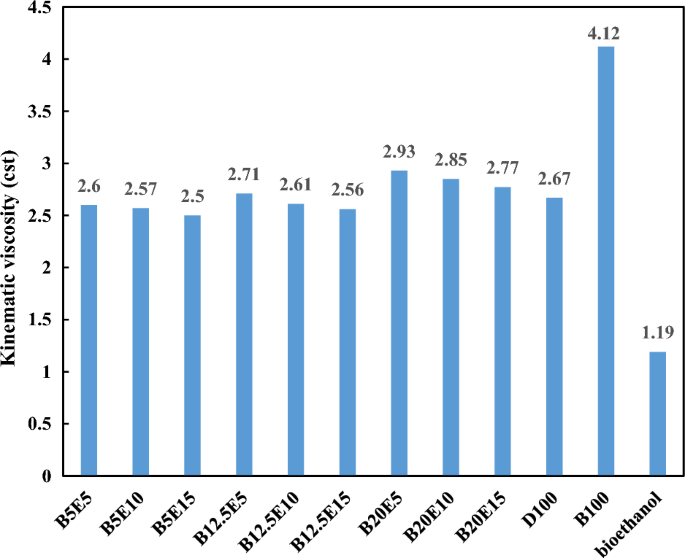
Figure 3 shows the kinematic viscosity of different fuel samples. The fuel viscosity is an important parameter which affects the spray quality and consequently the fuel and air mixing14. The viscosity of WFO biodiesel is higher compared to petro-diesel, which may leads to incomplete combustion by reducing the fuel and air mixing quality in the combustion chamber and increment in the exhaust emission3,32. Heat release rate (HRR) and cylinder pressure are the main combustion characteristics which are influenced by the fuel viscosity. Increasing the biodiesel content of the fuel blends leads to poor atomization of the fuel sample due to its high viscosity and results in an increment in the ignition delay and subsequent lower HRR and lower cylinder pressure33,34. On the other hand, the oxygen concentration of fuel blends is another parameter that affects the cylinder pressure. In this regard, the application biofuels leads to earlier combustion and improve the cylinder pressure due to increasing the oxygen content of the fuel blends35. According to Fig. 3, the kinematic viscosity of fuel blends increases by increasing the WFO biodiesel content and decreasing the bioethanol content of fuel blends, respectively. As an advantage, the viscosity of waste fish oil biodiesel is lower compared to calophyllum biodiesel by 87% and pongamia biodiesel by 48%8. It should be also noted that excessive reduction in the viscosity of fuel mixture is not desirable because it can be leads to…
Read More: Physical properties, engine performance, and exhaust emissions of waste fish oil